Electronics
Dispensing applications in the electronics industry
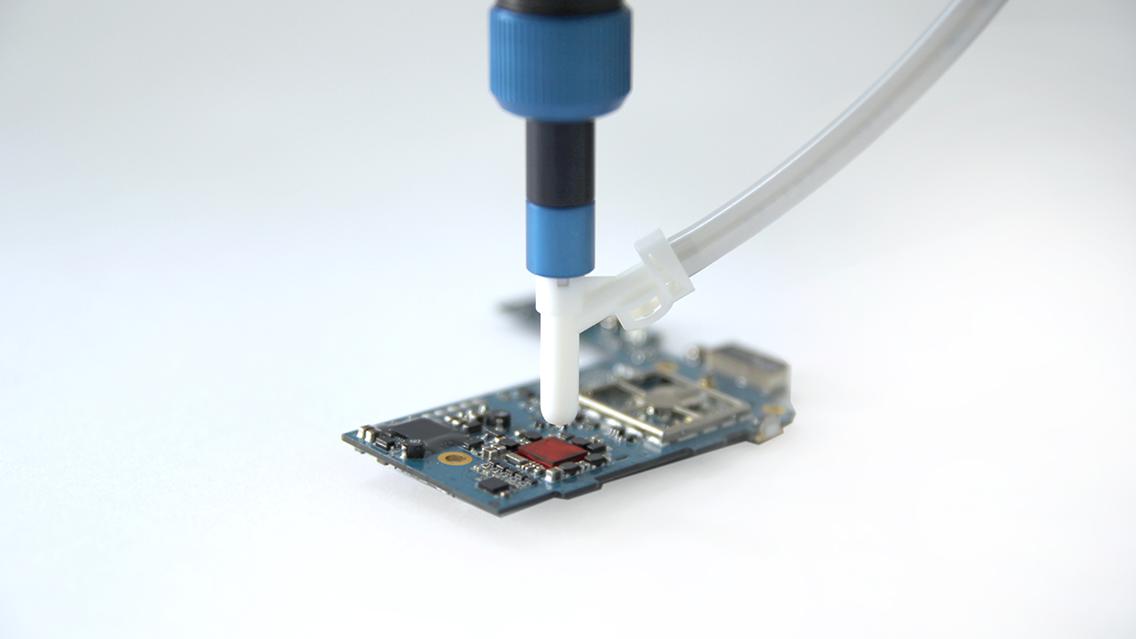
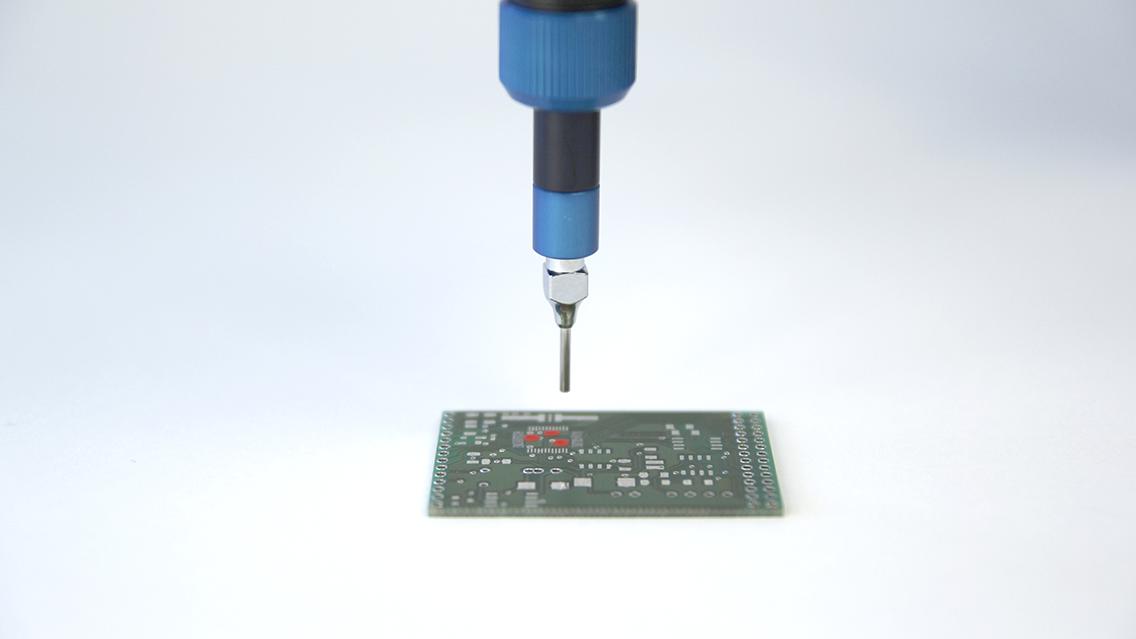
Micro dispensing systems in the electronics industry enable state-of-the-art manufacturing processes. And increase the service life of electronic components. Our dispensing systems are used, for example, to process adhesives, sealants, potting compounds, solder pastes or thermally conductive pastes. The performance requirements for ever smaller components and simultaneously decreasing manufacturing costs are constantly increasing. Fully automatic and process-safe micro dispensing systems like our ViscoTec and preeflow dispensing systems make this possible!
Liquids and pastes are dispensed purely volumetrically and handled extremely gently. Even solids-laden and shear-sensitive adhesives can be transported without any problems. And with a repeatability of 99 % – without air inclusions! For more information about our micro dispensing systems for the electronics industry, click here.
Application examples in the electronics industry:
LED potting / LED encapsulation
The material for LED encapsulation is usually low viscous. The pot life can vary from a few to many hours. ViscoTec’s pure volumetric endless piston principle guarantees high-precision, repeatable results. Excellent light output is a proof of the clean work of the dispensers. The shear-sensitive dispensing ensures that fillers remain completely intact.
To the application report about automated potting with Fichter-Maschinen.
Conformal coating
A conformal coating is a protective coating. It takes the form of a non-transparent or transparent varnish that is applied to a complete PCB or parts of PCBs. The materials are usually high-viscosity thermal or UV-curing materials. And are dosed onto the PCB using either a thin-film or a thick-film procedure.
To the preeflow application report with Panacol maskings and conformal coatings.
Dam & fill
In dam & fill applications, the primary aim is to protect highly complex assemblies. Firstly, a high-viscosity barrier, known as the “dam”, is applied to the surface to be sealed. Then the adjacent area is filled with a filler. And the area being dosed is sealed and protected by the fluid material.
To the preeflow application report about the fully automated dispensing system dispenseALL420.
Glob top
Glob-top potting is designed to protect sensitive components, usually semiconductor chips. It protects from mechanical stress such as vibrations or fluctuations in temperature. External environmental factors too, like moisture or corrosion, are thus prevented from having an impact on the potted components. This effect is realised by applying a fluid resin matrix, mostly an epoxy resin adhesive, which is then cured.
You are currently viewing a placeholder content from YouTube. To access the actual content, click the button below. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
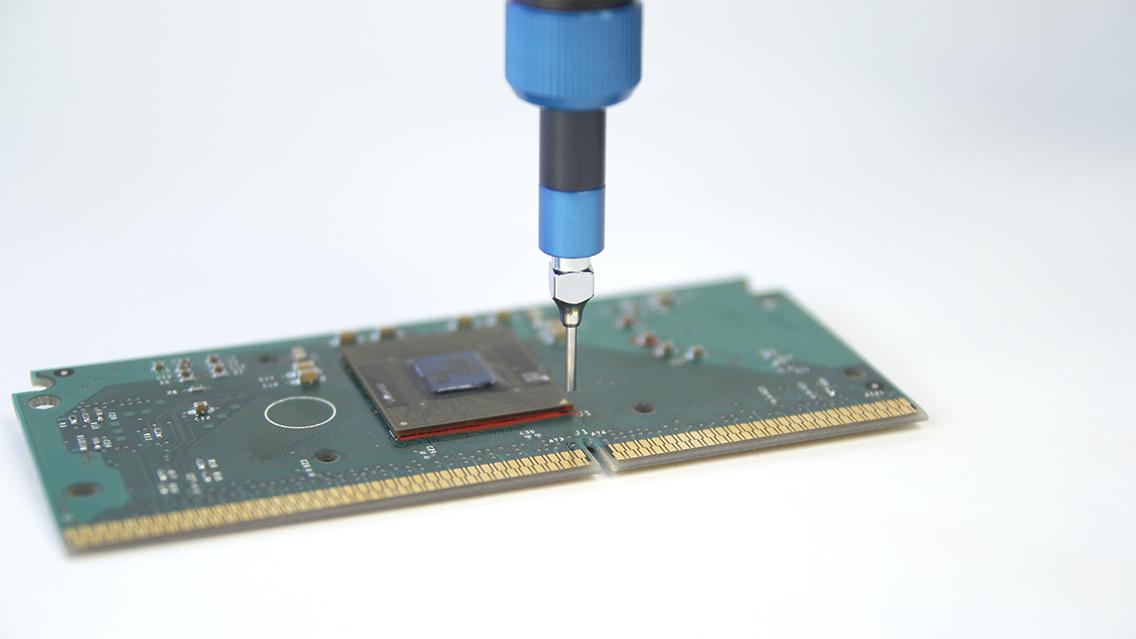
Microdispensing
Micro dispensing refers to the dosing of fluids or pastes in volume ranges of just a few microlitres. Fields of application are, for example, bead dosing, sealing, dot dosing, potting and 2-component applications. These applications in particular call for high levels of precision, repeat accuracy and reliability.
More about micro dispensing – for thermal management in printed circuit boards.
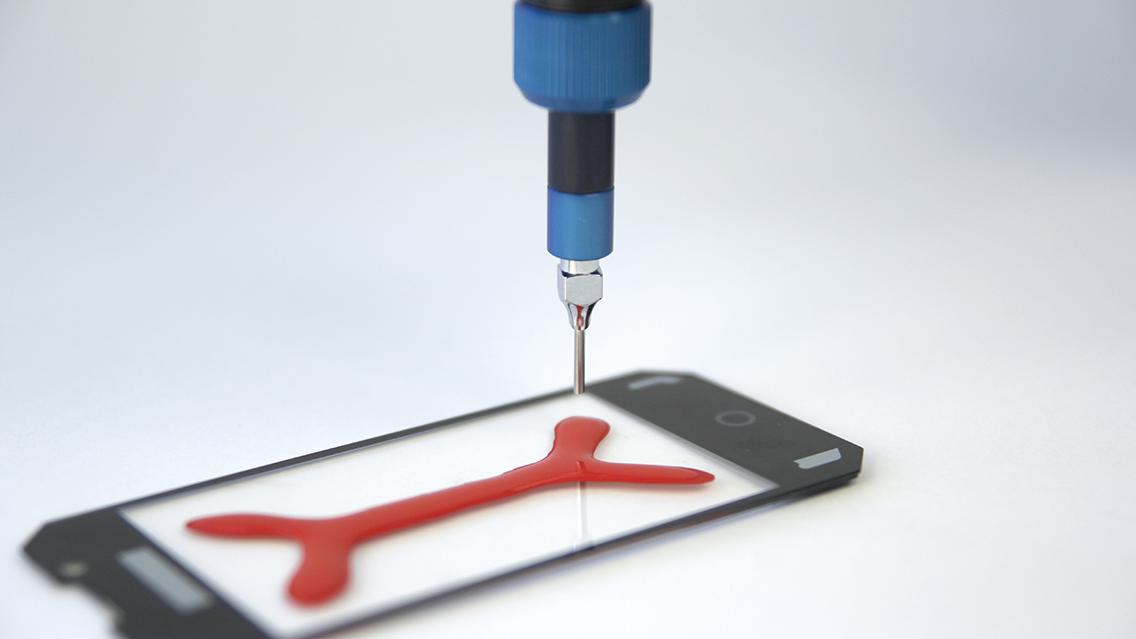
Optical bonding
Optical bonding is a process in which a clear adhesive is applied between the layers of glass in a touch-screen display. The main goal of this bonding process is to improve the performance of the display – for example outdoors. This procedure eliminates the gap between the glass and the display. A great deal of importance is placed on dosing precision in the field of smartphone and tablet manufacturing in particular.
You are currently viewing a placeholder content from YouTube. To access the actual content, click the button below. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
Underfill
Underfill applications are usually utilised with isotropic conductive adhesives. The isotropic conductive adhesive establishes the electrical connection between the microchip and the substrate. Since this adhesive is not applied over the entire surface, once it has cured (either thermally or by means of UV radiation), the hollow space needs to be refilled, or “underfilled”.
You are currently viewing a placeholder content from YouTube. To access the actual content, click the button below. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.